Our Treatments
we are team of oncologist who are expertise in all kind of surgery, Radiation and Chemotherapy.
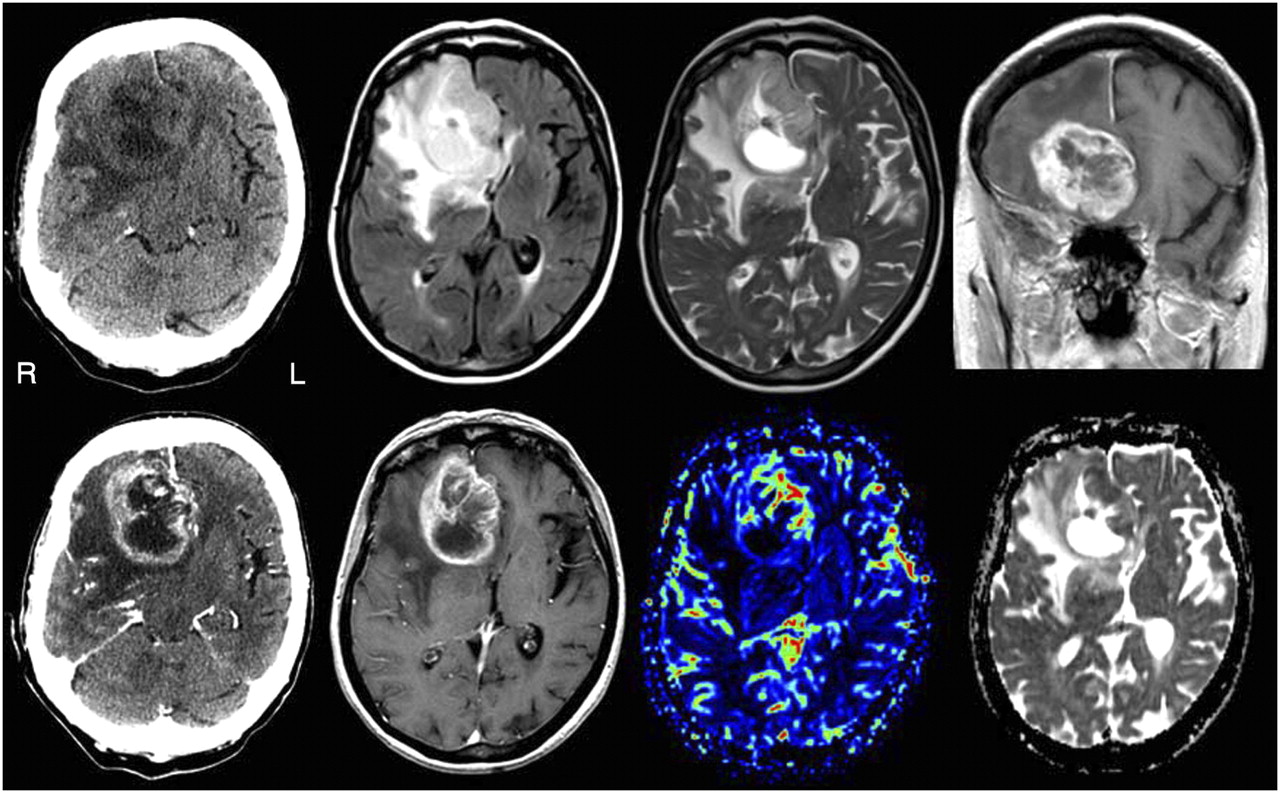
Brain Tumors - Malignant
A cancerous or non-cancerous mass or growth of abnormal cells in the brain, Brain tumors can be treated via Radiation therapy or Radiosurgery.
Radiation therapy uses proton energy beams to kill tumor cells. Usually an external beam radiation is used for this procedure which focuses just on the area of your brain where the tumor is located.
Symptoms include new or increasingly strong headaches, blurred vision, loss of balance, confusion and seizures. In some cases, there may be no symptoms
Head & Neck Cancer
Head and Neck Cancer is a common form of cancer in India. Every year more than one lakh case has been diagnosed in India. Types of Head & Neck cancers are listed below.
1. Oral Cavity, 2. Throat (pharynx), 3. Voice box (larynx), 4. Nasal Cavity, 5. Salivary glands, 6. Paranasal Sinuses.
Radiation Therapy is the primary treatment used to shrink a cancerous tumor. Either External Beam therapy (EBT) or Intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) procedure is used to treat these cancers.
Lung Cancer
Cancer that occurs in the Lungs are called Lung cancer. People who smoke have the greatest risk of lung cancer. Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy beams from sources such as X-rays and protons to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy may be used in combination with surgery and chemotherapy. Radiation therapy may help relieve symptoms, such as pain in patients with advanced stage of lung cancer.
Stereotactic radiosurgery may be an option for people with small lung cancers who can't undergo surgery or to treat cancers which have spread to other parts of the body.
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer can occur in women and rarely in men. Symptoms of breast cancer include a lump in the breast, bloody discharge from the nipple and changes in the shape or texture of the nipple or breast
Radiation therapy may be advised after surgery to remove the breast tumor (lumpectomy or mastectomy). Radiation can kill any cancer cells that might remain and reduce the risk of recurrence in the remaining tissues of the chest wall or lymph nodes. Radiation can be done for entire breast using External Beam Radiation Therapy or to the part of the breast using partial breast irradiation technique.

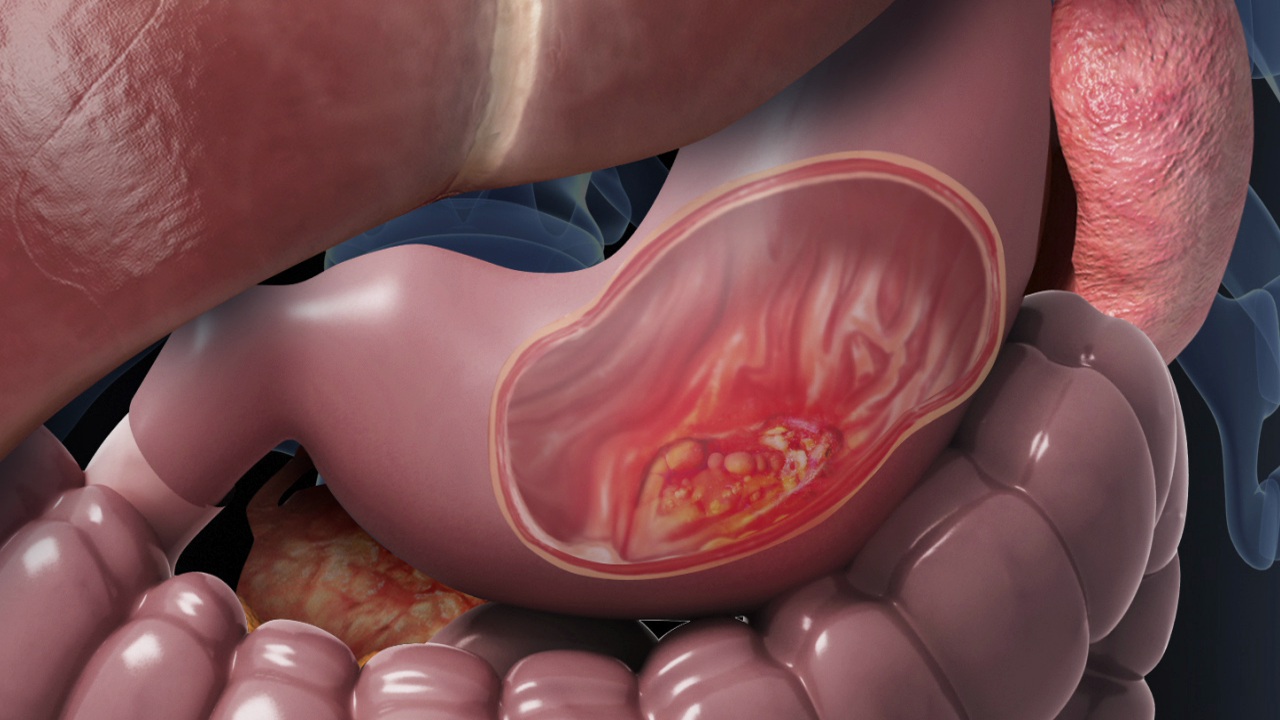
Gastrointestinal Cancer
Gastrointestinal cancer refers to malignant conditions of the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) and accessory organs of digestion, including the esophagus cancer, stomach cancer, biliary system, pancreas, small intestine cancer, large intestine cancer, rectum and anus
It can be used after surgery to kill any cancer cells that might remain. It can also be used before the surgery to shrink a large cancer so that it becomes easier to remove during surgery. For patients with advanced stage of cancer, radiation therapy might help to ease the pain and relieve some symptoms.
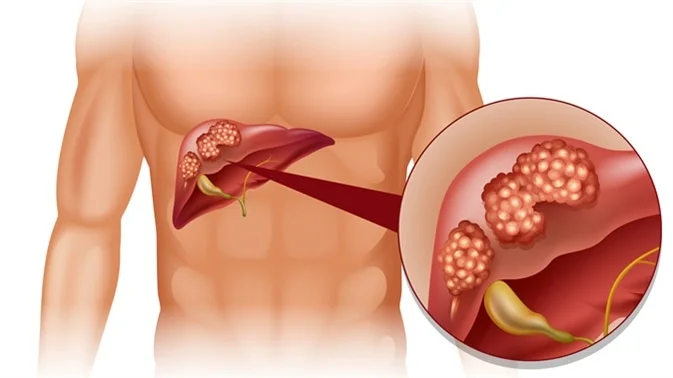
liver cancer & Pancreatic Cancer
Cancer of the pancreas is a disease in which malignant cells are found in the tissues of the pancreas. Hepatobiliary cancers refer to liver cancer and cancers of the biliary tract that occur in the bile ducts, the tubes that carry bile from the liver or gallbladder to the small intestine.
Hepatobiliary cancers are 1. Liver Cancer 2. Gallbladder Cancer 3. Bile Duct Cancer.
Pancreatic cancer types can be divided into broad type : 1. Exocrine pancreatic cancer, 2. Endocrine pancreatic cancer.
External beam radiation or Image Guide Radiation Therapy (IGRT) may be given to treat the above cancers in combination with chemotherapy.
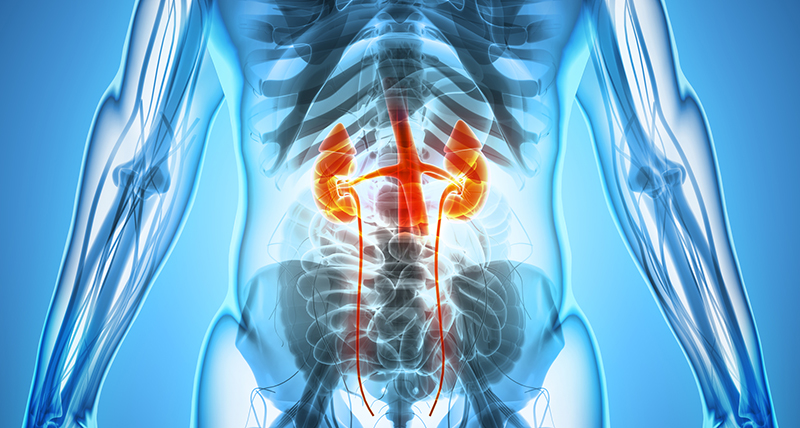
Male Genito-Urinary Cancers
Genitourinary cancers is a specialised field focusing on cancers found in the urinary system and the male reproductive system. These include prostate cancer, kidney cancer, bladder cancer, testicular cancer and cancers of the penis.
These cancers can be treated with External Beam Radiation Therapy, Brachytherapy, IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) or Proton beam therapy.
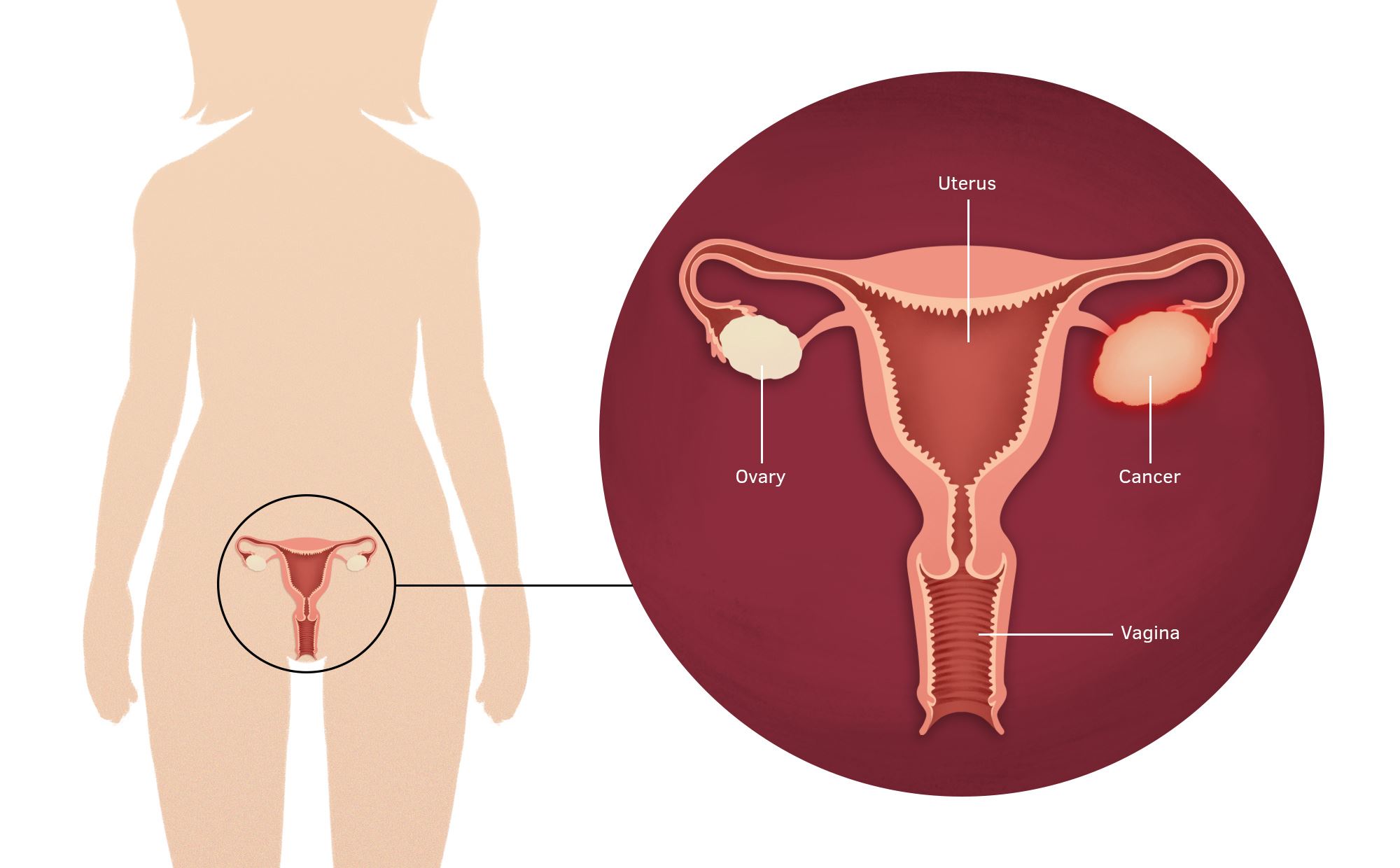
Female Genito-Urinary Cancers
When cancer starts in a woman's reproductive organs, it is called gynecologic cancer. The five main types of gynecologic cancer are: cervical, ovarian, uterine, vaginal, and vulvar.
They anchor to the adjacent teeth. Way they anchor to the adjacent teeth. Types of bridges may vary, depending upon how they are fabricated and the way.
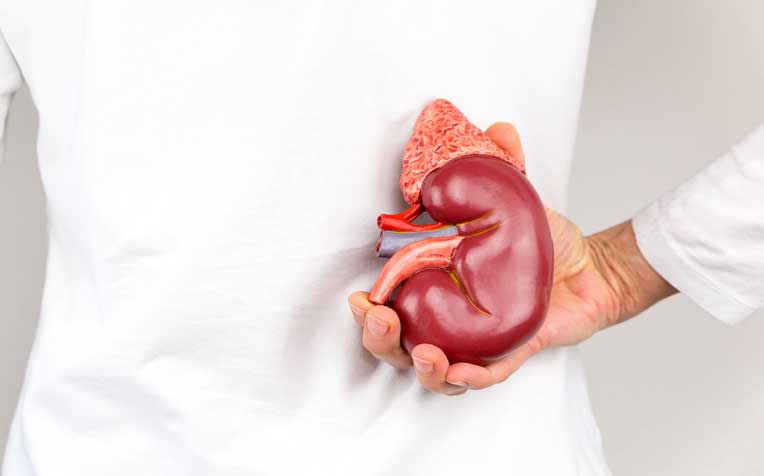
kidney cancer
Kidney cancer is cancer that begins in the kidneys. Your kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of your fist. In adults, renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer.
Kidney cancer usually doesn't have signs or symptoms in its early stages. In time, signs and symptoms may develop, including: Blood in your urine, which may appear pink, red or cola colored, Pain in your back or side that doesn't go away, Loss of appetite, Unexplained weight loss, Tiredness and Fever.
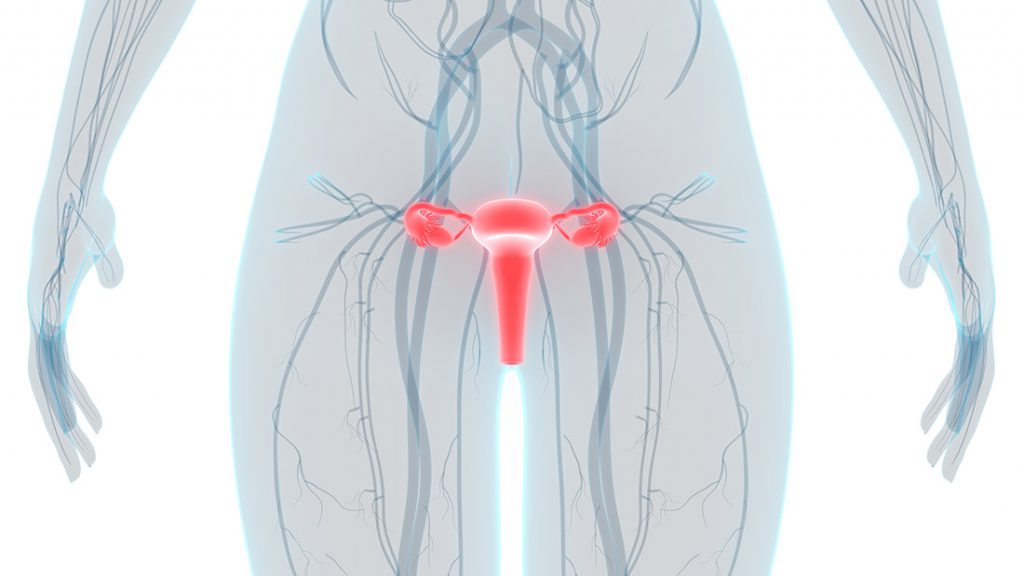
Gynecological cancer
Gynecologic cancer is any cancer that starts in a woman’s reproductive organs. Cancer is always named for the part of the body where it starts. Gynecologic cancers begin in different places within a woman’s pelvis, which is the area below the stomach and in between the hip bones.
Each gynecologic cancer is unique, with different signs and symptoms, different risk factors (things that may increase your chance of getting a disease), and different prevention strategies.
Blood cancer
Most blood cancers, also called hematologic cancers, start in the bone marrow, which is where blood is produced. Blood cancers occur when abnormal blood cells start growing out of control, interrupting the function of normal blood cells, which fight off infection and produce new blood cells.
Treatment for blood and bone marrow cancers depends on the type of cancer, your age, how fast the cancer is progressing, where the cancer has spread and other factors.
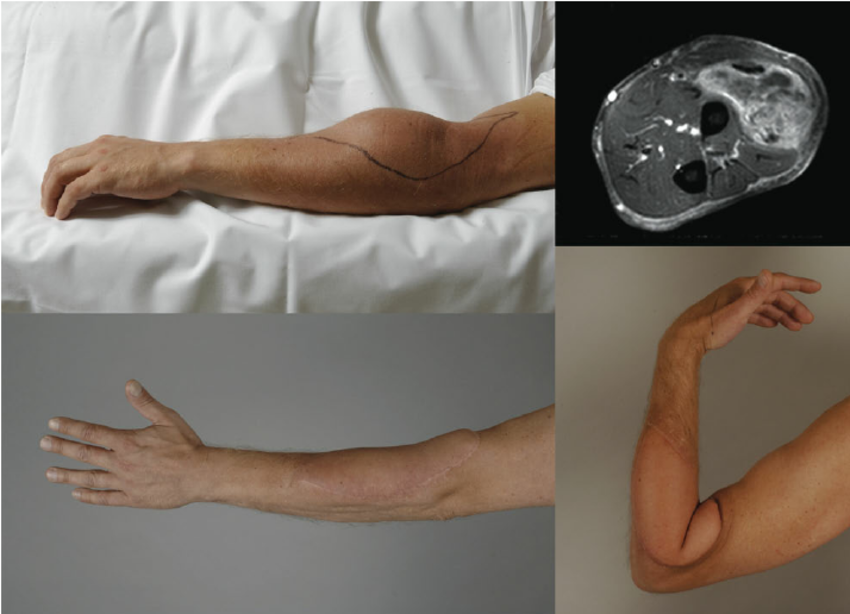
Sarcomas
Sarcoma is an umbrella term that is used to classify a broad number of cancers, and predominantly refers to bone cancer and connective/ soft tissue cancer in patients. It can affect many different parts of our body like: Muscles, Fats, Blood vessels, Nerves, Tendons, Joint lining, etc.
Sarcoma cancers can be treated with External Beam Radiation Therapy, Brachytherapy, IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) or Proton beam therapy.
Lymphoma
The lymphatic system is the body's disease-fighting network. It includes the lymph nodes, spleen, thymus gland and bone marrow. The main types of lymphoma are Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Lymphoma cancers can be treated with External Beam Radiation Therapy, Brachytherapy, IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) or Proton beam therapy.

Pediatric Tumors
Tumors of the brain or the tissue or structures that surround it as found in children are pediatric brain tumors. Pediatric brain tumors can be noncancerous (benign) or malignant (cancerous).
Lymphoma cancers can be treated with External Beam Radiation Therapy, Brachytherapy, IMRT (Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy) or Proton beam therapy.
Diagnosis
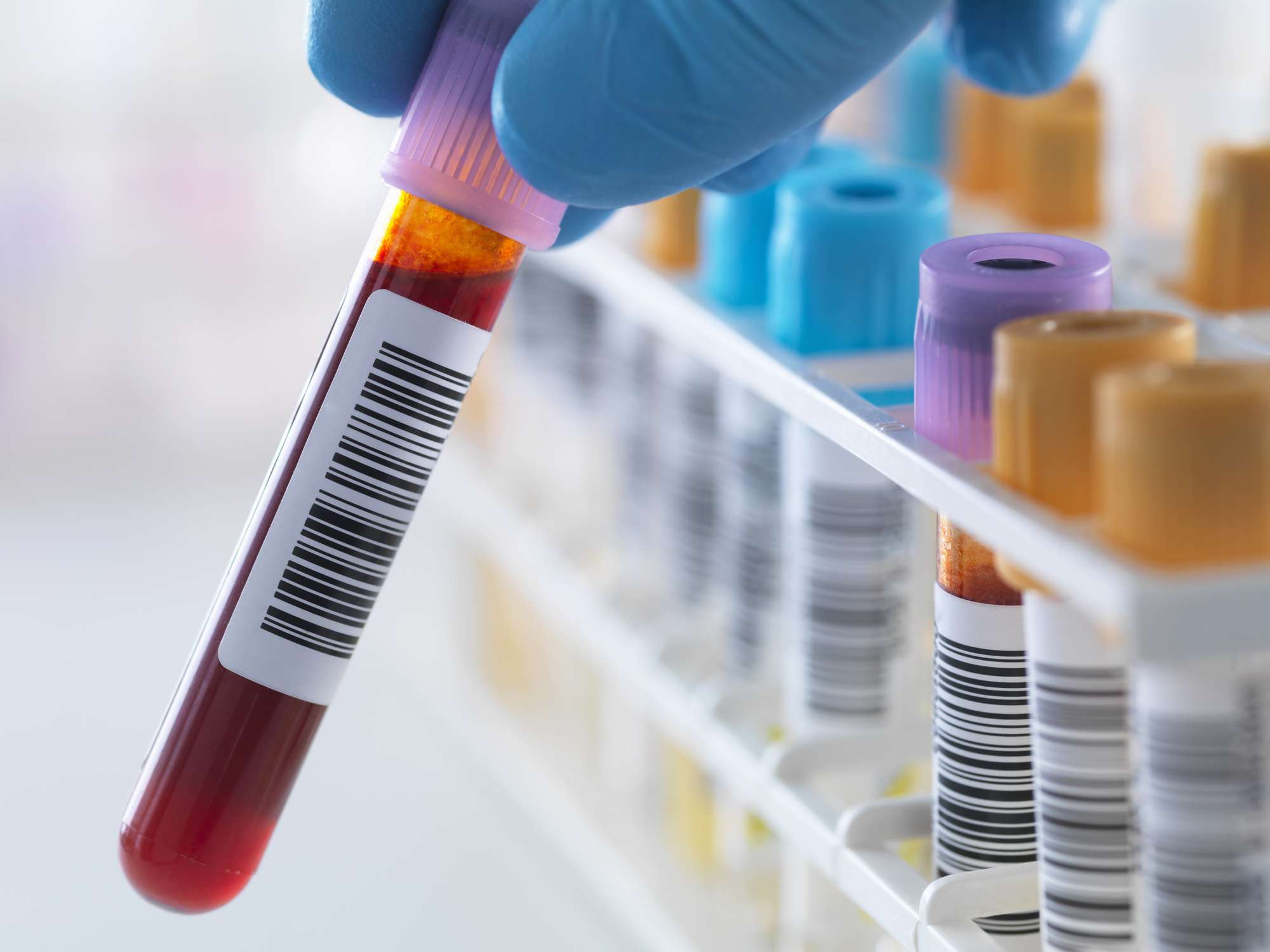
Blood Tests
Cancer blood tests and other laboratory tests may help your doctor make a cancer diagnosis. Reduce your anxiety by learning about cancer blood tests
Blood tests used to diagnose cancer include:
- Complete blood count (CBC)
- Blood protein testing
- Tumor marker tests
- Circulating tumor cell tests
Biopsy
A biopsy is a procedure to remove a piece of tissue or a sample of cells from your body so that it can be tested in a laboratory. You may undergo a biopsy if you're experiencing certain signs and symptoms or if your health care provider has identified an area of concern. A biopsy can determine whether you have cancer or another condition.
Imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, are helpful in detecting masses or irregular tissue, but they alone can't tell the difference between cancerous cells and cells that aren't cancerous.
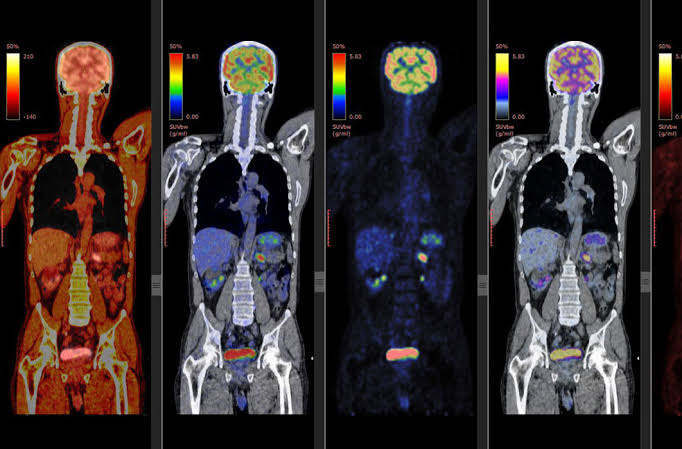
PET-CT scan
Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers or radiopharmaceuticals, a special camera and a computer to evaluate organ and tissue functions. By identifying changes at the cellular level, PET may detect the early onset of disease before other imaging tests can.
For some types of cancer, a PET-CT scan is a way to help find cancer and learn its stage. Stage is a way to describe where the cancer is and if it has spread. Doctors also learn information about the stage if and how the cancer is affecting your body's functions.
Get an appointment for scan
Call now